Cell- Fundamental Unit Of Life Class 9 Chapter 5
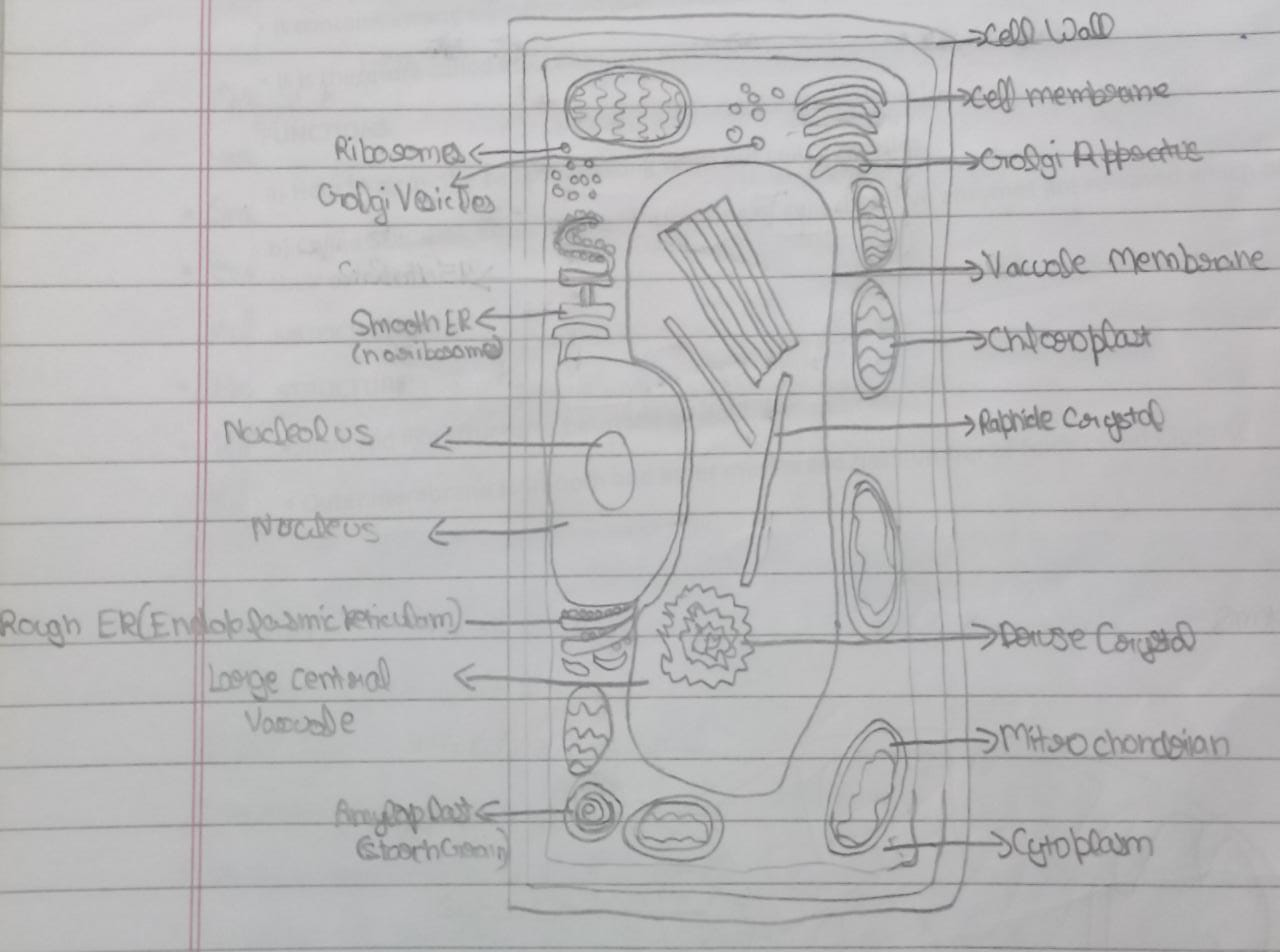
Cell Wall
- It is the outer most covering of Plant cells. i.e. present outside the Plasma Membrane
- It is absent in Animal Cell
- It is rigid, strong, porous and non- living structure
- It is made up of Cellulose (Complex fibrous Carbohydrate)
- Cell wall of two adjacent cells are joined by a layer Lamellae
FUNCTIONS OF CELL WALL
- Cell wall provides mechanical strength and shape to plants.
- Cell wall prevents bursting of cell on Endosmosis. As water enters living cells their protoplasm swells up and builds pressure against the cell wall. The cell wall exerts an equal and opposite pressure against the cell. As a result further entry of water into cells is stopped. Hence, Cell wall helps plants to withstand in very dilute (Hypotonic) solution.
Plasmolysis- When a living plant cell loses water through osmosis there is shrinkage or contraction of the contents of the cell away from the cell wall. This phenomenon is called plasmolysis.
Nucleus (Head-Quarter of Cell)
- It has a double layered covering called nuclear membrane.
- Nuclear membrane has pores which regulate the movement of material in out of nucleus.
- Inside nuclear membrane it contain- Nucleolus, Chromosomes and Chromatin
- Chromatin material consist of DNA (Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid) and Protein.
- Chromosomes contain information for inheritance of features from parents to next generation.
- Functional segment of chromosome which contain information are called Genes.
- It controls and directs the Cellular Activities.
Nucleolus- Present in the centre of nucleus and consist of Ribosomes.
Ribosomes- Ribosomes are yellow dot. Like structure helps in the formation of Proteins.